(For the very latest variant surveillance, check here. The latest variant is the Omicron variant.)
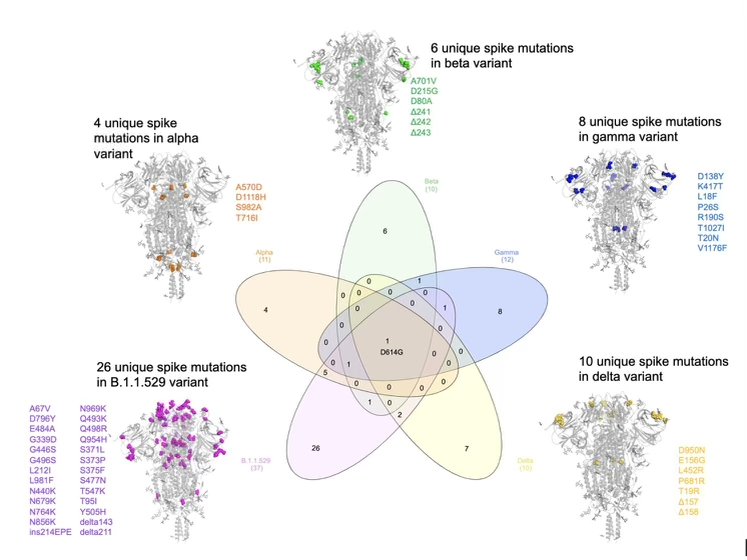
Coronavirus was first spotted in Wuhan, China, in late 2019. The original virus has mutated many times since then, leading to variants. Some mutants are more dangerous than others (namely the Delta mutant, believed to be much more contagious and possibly more deadly).
| Country first noticed | Variant | Technical Name/Lineage |
|---|---|---|
| China (origin) | –– | Parent Genome |
| U.K. | Alpha | B.1.1.7 |
| South Africa | Beta | B.1.351 |
| India | Kappa | B.1.617.1 |
| India | Delta | B.1.617.2 |
| Peru | Lambda | C.37 |
| Japan | Gamma | P.1 |
| Columbia | Mu | B.1.621 |
| South Africa | Omicron | B.1.1.529 |
When a virus makes copies of itself, it can make random mistakes as it goes along spreading from host to host. Most mistakes either weaken the virus or have no effect on it. Occasionally, a mistake can actually bestow a benefit to the virus. The Delta variant is a good example of this. Over time, this strain has accumulated mutations (or mistakes) that make it better at infecting humans. This makes it more dangerous to the general population, especially to people who haven’t been fully vaccinated.
updated 12-06-21
© Copyright 2021. All Rights Reserved. ScoreMatrix • Designed by Nash